 2 March, 2025
2 March, 2025
Understanding ECMO: A Lifesaving Option for Patients with Compromised Heart Function
In today’s discussion, we delve into the world of ECMO, a cutting-edge technology that holds promise for patients grappling with compromised heart function. Join Dr. Dhamodaran as he unpacks the mechanics of ECMO and its potential to transform patient outcomes.
Introduction to ECMO
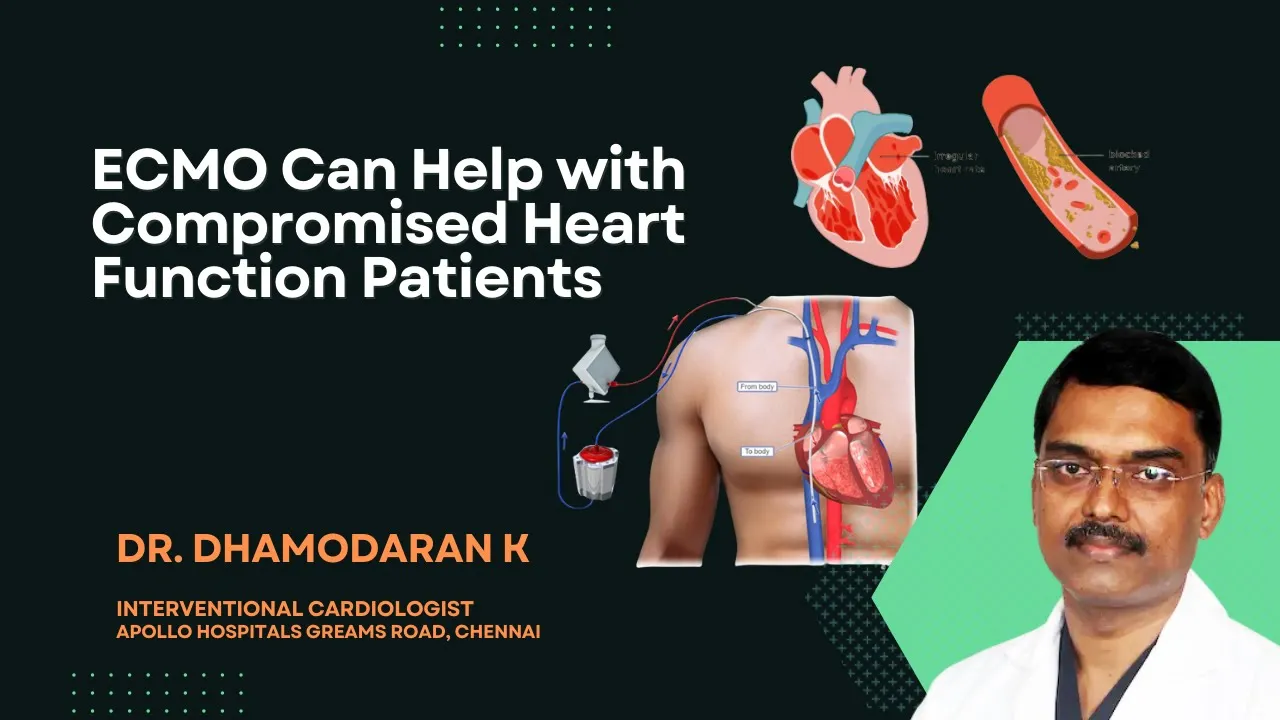
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) is a sophisticated life-support system that provides both cardiac and respiratory support to patients whose heart and lungs are severely compromised. This advanced technology is often utilized in critical care settings where traditional methods fail to provide adequate support. ECMO acts as an artificial heart and lung, performing the functions of these vital organs while allowing them to rest and heal.
What is Compromised Heart Function?
Compromised heart function refers to a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to inadequate blood flow to meet the body’s needs. This can result from various medical conditions, including severe heart attack, cardiomyopathy, or congenital heart defects. Symptoms may manifest as fatigue, shortness of breath, or fluid retention, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life.
How ECMO Works
The ECMO system consists of a pump and an oxygenator, which together facilitate the removal of carbon dioxide and the addition of oxygen to the blood. Blood is drawn from the body, passed through the oxygenator, and then returned to the patient. This process mimics the natural functions of the heart and lungs, ensuring that tissues receive the oxygen they need while removing waste products efficiently.
Components of ECMO
- Pump: Circulates blood through the system.
- Oxygenator: Enriches blood with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
- Catheters: Inserted into major blood vessels to connect the patient to the ECMO machine.
Benefits of ECMO for Patients
ECMO offers several vital benefits for patients with severe heart and lung failure. It allows for longer recovery times without the strain on the heart and lungs. Furthermore, it can provide a bridge to recovery or transplantation, giving patients more time to heal or wait for a suitable donor organ.
Key Advantages
- Improved Oxygenation: Ensures adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
- Organ Rest: Allows the heart and lungs to recover from injury.
- Time for Treatment: Provides crucial time for other therapies or surgical interventions.
Who Can Benefit from ECMO?
ECMO is not suitable for every patient, but it can be a lifesaving option for those with specific conditions. Patients suffering from severe respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, or those awaiting heart or lung transplants may be candidates for ECMO. The decision to initiate ECMO is made by a specialized team based on the patient’s overall health, prognosis, and specific needs.
Potential Candidates
- Patients with severe pneumonia or ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome).
- Individuals experiencing cardiogenic shock or severe heart failure.
- Patients awaiting lung or heart transplantation.
The ECMO Procedure Explained
The ECMO procedure begins with the insertion of catheters into the patient’s blood vessels. This is typically done in a controlled environment, such as an intensive care unit. Once the ECMO machine is connected, it takes over the role of pumping and oxygenating the blood, allowing medical professionals to monitor and manage the patient’s condition closely.
Steps in the ECMO Procedure
- Patient Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s condition.
- Catheter Insertion: Placement of catheters into the appropriate blood vessels.
- ECMO Connection: Linking the patient to the ECMO machine.
- Monitoring: Continuous observation and adjustment of settings as needed.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While ECMO presents numerous benefits, it is not without risks. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for patients and their families when considering this life-saving option.
Common Risks Associated with ECMO
- Bleeding: The use of anticoagulants to prevent blood clots can lead to significant bleeding complications.
- Infection: Catheter insertion points and the ECMO circuit itself can become sources of infection.
- Organ Dysfunction: Prolonged support can potentially lead to dysfunction in other organs, particularly the kidneys.
- Neurological Events: There is a risk of stroke or other neurological complications due to changes in blood flow.
Factors Influencing ECMO Suitability
Not every patient is an ideal candidate for ECMO. A thorough evaluation by a specialized medical team considers various factors, including:
- Underlying health conditions.
- Likelihood of recovery.
- Overall prognosis and quality of life post-ECMO.
Patient Stories: Success with ECMO
Real-life stories of patients who have undergone ECMO highlight its transformative potential. These narratives not only inspire hope but also provide insight into the journey of recovery.
Case Study 1: Overcoming Severe Respiratory Failure
A 35-year-old woman, diagnosed with severe pneumonia, faced life-threatening respiratory failure. After being placed on ECMO, she experienced a gradual improvement in her oxygen levels. Within weeks, she was able to breathe independently and eventually returned to her normal life, expressing immense gratitude for the second chance.
Case Study 2: A Heart Transplant Journey
An elderly man with end-stage heart failure awaited a transplant. ECMO provided the necessary support, allowing his heart to rest while he waited for a donor. After several weeks, he received a new heart and credits ECMO for giving him the time he needed to survive and thrive.
Future of ECMO Technology
The field of ECMO technology is continually evolving, promising even greater advancements in patient care.
Innovations on the Horizon
- Miniaturization: New designs aim to create smaller, more portable ECMO devices, enhancing mobility for patients.
- Biomaterials: Research into biocompatible materials may reduce complications associated with the ECMO circuit.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI integration could improve monitoring and decision-making, optimizing patient outcomes.
Potential Impact on Patient Outcomes
As ECMO technology advances, we anticipate improved survival rates and reduced complications. These innovations may increase accessibility, allowing more patients to benefit from this life-saving therapy.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
ECMO represents a beacon of hope for patients facing severe heart and lung challenges. With its ability to provide essential support, it opens doors to recovery and rehabilitation. However, it is vital to weigh the benefits against potential risks carefully.
As technology progresses, the future of ECMO looks promising. Ongoing research and innovation will undoubtedly enhance its effectiveness and safety. For patients and families, understanding ECMO is crucial in making informed decisions about treatment options.
FAQs about ECMO
What is the typical duration of ECMO support?
The duration of ECMO support varies based on the patient’s condition and response to treatment, ranging from days to weeks.
Can ECMO be used for children?
Yes, ECMO is used in pediatric patients, often with specially designed systems tailored for their unique needs.
What happens after ECMO is discontinued?
Post-ECMO, patients undergo careful monitoring and rehabilitation to ensure a smooth transition back to normal activities.
Are there long-term effects after ECMO?
Some patients may experience long-term effects, including physical and psychological challenges. Ongoing support is essential for recovery.
Consultation Location

 +91 96001 07057
+91 96001 07057 Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020

