 21 November, 2025
21 November, 2025
When the Heart Fails, the Kidneys and Lungs Follow: The Hidden Domino Effect Inside the Body
Modern cardiology is no longer just about the heart alone. The heart, kidneys, and lungs are deeply interlinked. When one falters, the others often follow. This “domino effect” is especially visible in patients with acute cardiac illness, heart failure, or post-PCI recovery challenges.
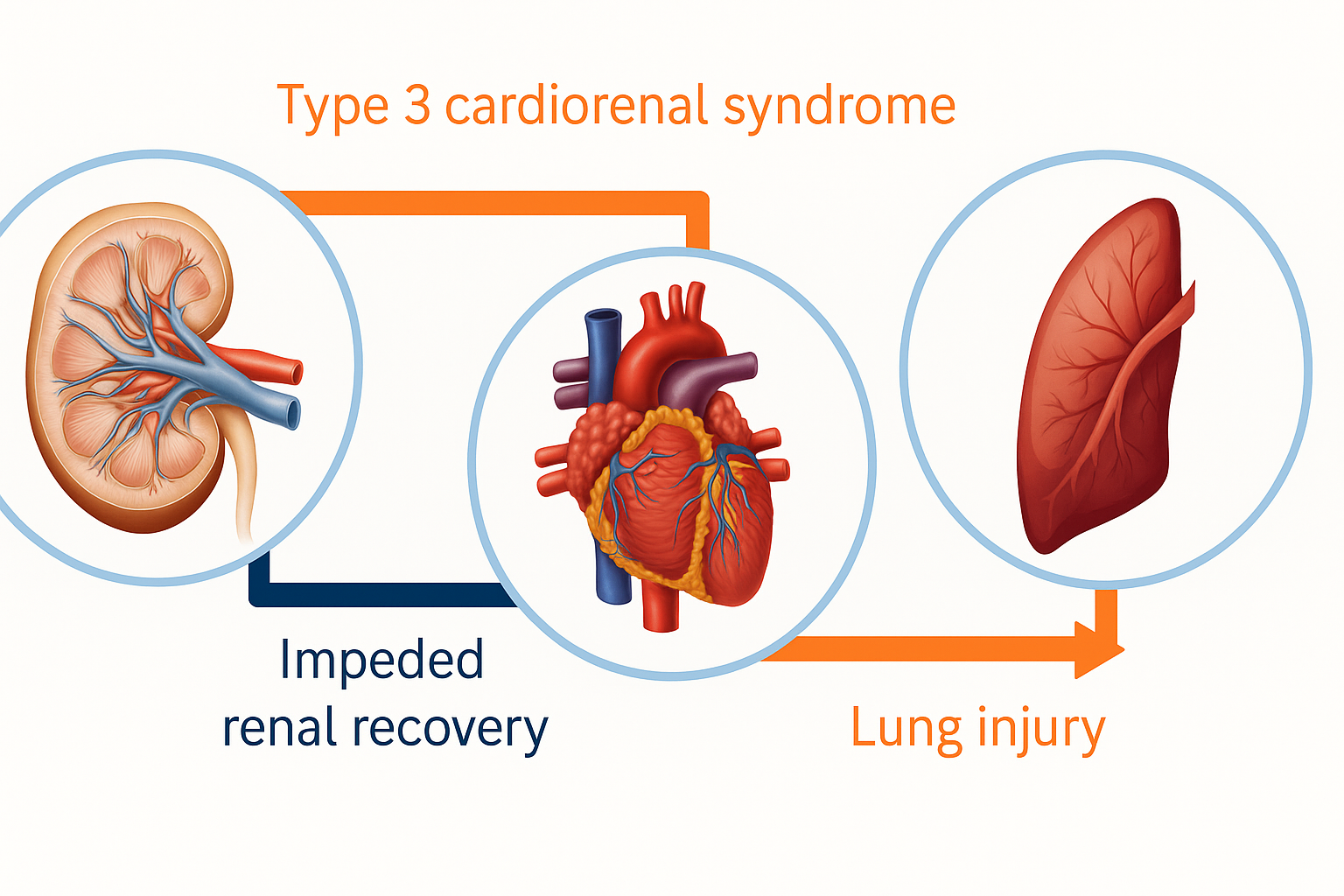
The image above captures this perfectly:
Heart → Kidney → Lung
A single organ under stress can trigger a chain reaction, often silently, until symptoms become severe.
Let’s unpack this hidden trilogy.
1. The Heart at the Centre of the Storm
The heart’s job is simple on the surface—pump blood. But this pump drives oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to every organ. When the heart slows down or becomes weak (as in acute decompensated heart failure, cardiogenic shock, myocardial injury, or ischemia):
-
Blood flow to the kidneys drops.
-
Venous pressures rise.
-
Inflammatory markers shoot up.
-
Fluid accumulates in the lungs.
Your heart might be the first to struggle… but it’s rarely the last to suffer.
2. Type 3 Cardiorenal Syndrome: When Kidney Injury Begins in the Heart
One of the most misunderstood conditions is Type 3 Cardiorenal Syndrome—a disorder where sudden kidney dysfunction triggers acute heart problems.
But the opposite is also true:
Acute heart injury can impair renal recovery, even in patients who initially had normal kidney function.
How the Heart Affects the Kidneys
-
Reduced cardiac output means less blood reaches the kidneys.
-
Persistent congestion puts pressure on renal veins.
-
Neurohormonal systems (RAAS, sympathetic drive) activate aggressively.
-
Kidneys retain salt and water trying to “compensate,” actually worsening heart failure.
It’s a vicious cycle.
The kidneys are not just victims—they become amplifiers of heart dysfunction.
This is why modern interventional cardiology emphasises ultra-low contrast PCI, hemodynamic-guided therapy, and early renal protection strategies.
3. Lung Injury: The Final Organ in the Chain Reaction
Once the kidneys fail to regulate fluid effectively, the lungs become the next organ to feel the burden.
Why the Lungs Get Affected
-
Excess fluid backs up into pulmonary circulation.
-
Oxygen exchange becomes inefficient.
-
Patients develop shortness of breath, hypoxia, or even acute respiratory distress.
-
Kidney dysfunction worsens acidosis, further stressing lung function.
This is why cardiologists often say:
“Heart failure is not a heart disease. It is a multi-organ disease.”
4. The Real Danger Lies in the Combination
Each organ—heart, kidney, lung—can fail independently.
But when two or more fail together, the outcome becomes significantly worse.
What Makes This Trio Dangerous
-
Treatment becomes complex.
-
Fluid balance becomes unpredictable.
-
Decisions about diuretics, vasodilators, or inotropes become high-risk.
-
Even small medical errors can precipitate a cascade of deterioration.
This is why high-risk patients (CKD, diabetics, elderly, post-MI, severe LV dysfunction) require:
-
Precision-guided PCI
-
Minimal contrast strategies
-
Renal protection protocols
-
Early respiratory monitoring
Modern cardiology is moving toward organ-preserving interventions, not just artery-opening procedures.
5. What Patients Should Know
Kidney and Lung Symptoms Can Start With the Heart
One may not feel chest pain at all, yet still develop:
-
Sudden breathlessness
-
Fatigue
-
Swelling in legs
-
Reduced urine output
-
Confusion
-
Worsening sleep due to breathlessness
All these can be warning signs of the domino effect in progress.
Early Detection Saves Organs
Simple diagnostics can help identify the danger early:
-
Creatinine levels
-
Urine output monitoring
-
BNP/NT-proBNP
-
Chest X-ray or lung ultrasound
-
Daily weight and fluid balance
-
Echocardiography
6. The Way Forward: Multi-Organ Care is the Future of Cardiology
Cardiology is evolving beyond “fixing blockages.”
Interventional teams today focus on:
-
Protecting kidneys during PCI
-
Monitoring lungs during acute decompensation
-
Fluid-smart, contrast-smart therapy
-
Advanced hemodynamic support
-
Multidisciplinary teams (heart–kidney–lung specialists)
Patients are living longer because cardiologists are treating the entire system—not just the heart muscle.
 +91 96001 07057
+91 96001 07057 Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
