 24 January, 2025
24 January, 2025
Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (CTO PCI): A Comprehensive Guide to Heart Health and Angioplasty
Introduction
Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) of the coronary arteries represents one of the most challenging forms of coronary artery disease. Characterized by a 100% blockage of a coronary artery for a prolonged period (typically more than three months), CTO can significantly affect heart function and a patient’s quality of life. Fortunately, advancements in interventional cardiology, particularly Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), have revolutionized the treatment of CTO, offering patients new hope and improved outcomes.
This comprehensive guide explores CTO PCI, its significance, procedure, benefits, risks, and post-procedure care, providing valuable insights for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
Understanding CTO and PCI
What is CTO?
CTO refers to a complete blockage in one of the coronary arteries, usually caused by atherosclerosis. Over time, fatty deposits (plaques) build up in the arterial walls, leading to restricted blood flow. When untreated, CTO can result in chest pain (angina), reduced exercise tolerance, or even heart failure.
What is PCI?
PCI, commonly known as angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked coronary arteries. During PCI, a catheter is inserted into the artery, and a small balloon is inflated to clear the blockage. Often, a stent is placed to keep the artery open, ensuring normal blood flow.
When PCI is specifically applied to treat CTO, it is referred to as CTO PCI. This highly specialized procedure requires advanced techniques and expertise to navigate the chronic blockage.
The CTO PCI Procedure
1. Pre-Procedure Evaluation
- Diagnosis: A thorough diagnosis typically involves imaging techniques such as coronary angiography, stress tests, or advanced imaging like CT coronary angiograms.
- Risk Assessment: Doctors evaluate the patient’s overall health, underlying conditions, and the complexity of the blockage.
- Medication Adjustment: Patients may need to discontinue certain medications, such as blood thinners, prior to the procedure.
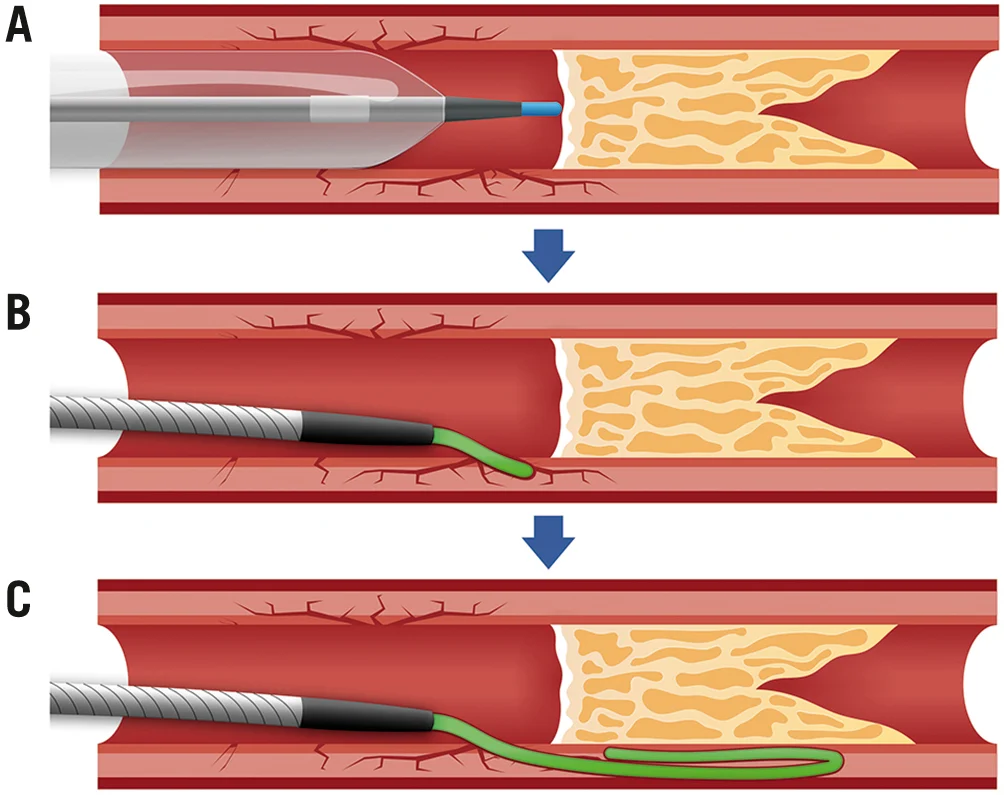
2. During the Procedure
- Accessing the Artery: The cardiologist inserts a catheter through a small incision, usually in the wrist or groin.
- Navigating the CTO: Using guide wires, the specialist carefully advances through the blocked artery.
- Clearing the Blockage: A balloon catheter is used to compress the plaque. In most cases, a stent is deployed to ensure long-term patency.
- Imaging Guidance: Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) or optical coherence tomography (OCT) may be used to improve precision.
3. Post-Procedure Care
- Patients are monitored for a few hours or overnight to ensure there are no complications.
- Medications like antiplatelets are prescribed to prevent blood clots.
Benefits of CTO PCI
- Symptom Relief
- Alleviates chronic chest pain and discomfort.
- Improved Heart Function
- Restores blood flow to the heart, improving overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Quality of Life
- Patients often experience better exercise tolerance and daily functioning.
- Minimally Invasive
- Compared to open-heart surgery, CTO PCI involves shorter recovery times and reduced risks.
Risks and Complications
While CTO PCI has high success rates in experienced hands, it’s not without risks:
- Bleeding: At the catheter insertion site.
- Blood Vessel Damage: Rarely, guide wires or balloons can damage the artery.
- Heart Attack: Though uncommon, the procedure can sometimes trigger a heart attack.
- Stent Thrombosis: Clots forming in the stent require urgent medical attention.
Recovery and Post-Procedural Care
- Immediate Care:
- Patients may need to lie flat for a few hours to prevent bleeding from the insertion site.
- Heart rate and blood pressure are monitored closely.
- Medications:
- Antiplatelets (e.g., aspirin and clopidogrel) are prescribed to prevent clot formation.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) may be recommended.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Begin light activity after consulting with the doctor.
- Smoking Cessation: Essential for improving heart health.
- Follow-Up Appointments:
- Regular check-ups ensure the stent remains functional and assess overall cardiac health.
Advances in CTO PCI Techniques
- Retrograde Approach:
- Accessing the blockage from a collateral artery when the primary route is inaccessible.
- Hybrid Algorithm:
- Combines various approaches for personalized treatment plans.
- Robotic-Assisted PCI:
- Enhances precision and reduces radiation exposure to the medical team.
- Drug-Eluting Stents:
- These stents release medication to prevent re-narrowing of the artery.
When to Consider CTO PCI
- Severe Angina:
- Persistent chest pain despite medication.
- Reduced Quality of Life:
- Inability to perform routine activities due to heart-related symptoms.
- Failed Medical Therapy:
- When lifestyle changes and medications fail to manage symptoms.
FAQs about CTO PCI and Angioplasty
1. What is the success rate of CTO PCI?
- The success rate ranges from 85% to 90% in experienced centers. Advances in techniques and technologies have significantly improved outcomes.
2. Is CTO PCI painful?
- The procedure itself is not painful as it is performed under local anesthesia. Patients may feel mild discomfort at the catheter insertion site.
3. How long does the procedure take?
- CTO PCI can take 2 to 4 hours depending on the complexity of the blockage.
4. What is the recovery time for CTO PCI?
- Most patients can return to light activities within a week and resume normal routines in two weeks. However, recovery may vary based on individual health.
5. Are there alternatives to CTO PCI?
- Alternatives include medical management with drugs, lifestyle modifications, or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) for severe cases.
6. Can CTO PCI prevent heart attacks?
- While CTO PCI restores blood flow and improves symptoms, it’s not a guarantee against future heart attacks. Regular follow-ups and a heart-healthy lifestyle are crucial.
7. What happens if a stent fails?
- Stent failure (restenosis or thrombosis) may require repeat angioplasty, stent replacement, or other interventions.
8. Who is not a candidate for CTO PCI?
- Patients with severe comorbidities, poor overall prognosis, or unsuitable anatomy may not qualify. A cardiologist will evaluate individual cases.
9. Can I live a normal life after CTO PCI?
- Yes, most patients experience significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life. Adhering to medical advice is key to long-term success.
10. What are the costs involved?
- The cost of CTO PCI varies based on location, healthcare facility, and insurance coverage. Consult with your provider for detailed cost information
Consultation Location

 +91 96001 07057
+91 96001 07057 Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020

