 28 June, 2025
28 June, 2025
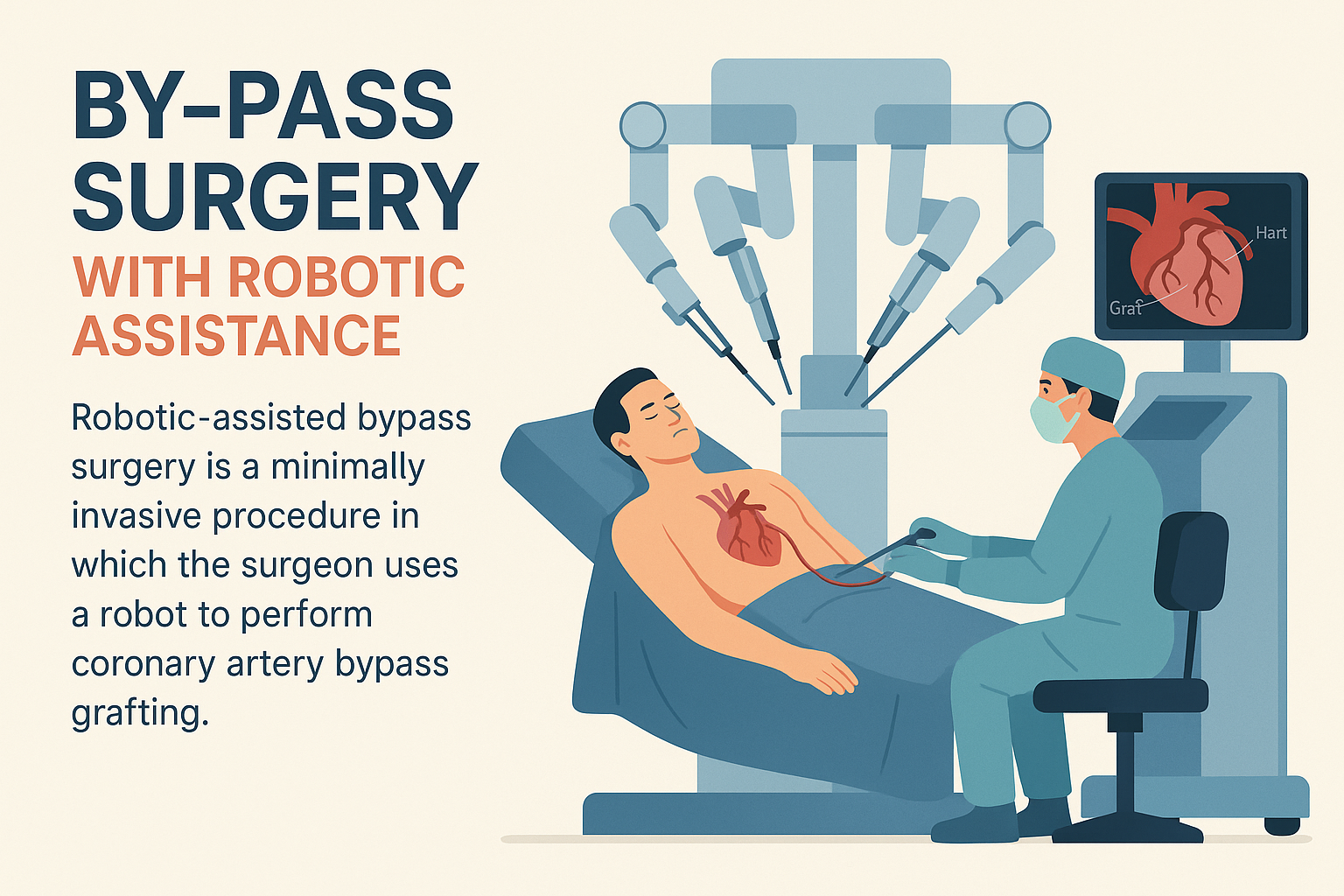
Robotic-Assisted Bypass Surgery: A Safer, Smarter Way to Mend the Heart
Heart disease continues to be one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), commonly known as bypass surgery, remains one of the most effective treatments for patients with severe coronary artery blockages. Traditionally, bypass surgery is a major open-heart procedure. But with advancements in medical technology, robotic-assisted bypass surgery is now offering a less invasive, more precise alternative.
If you or a loved one has been advised to undergo bypass surgery, understanding how robotic assistance works can help ease anxiety and empower you to make informed decisions.
What is Bypass Surgery?
Bypass surgery involves creating a new path (or “bypass”) around blocked or narrowed arteries so that blood can flow freely to the heart. Surgeons usually use a healthy blood vessel from the patient’s leg, arm, or chest and connect it beyond the blockage in the coronary artery.
In traditional surgery, this involves opening the chest through a large incision and sometimes even stopping the heart to complete the procedure. While effective, recovery is often long and physically demanding.
What is Robotic-Assisted Bypass Surgery?
Robotic-assisted bypass surgery is a minimally invasive technique where the surgeon uses a robotic system to perform the operation through small incisions. One of the most common robotic procedures is Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass (TECAB).
Here’s how it works:
-
The surgeon controls a robotic arm from a console while viewing a high-definition, 3D image of the heart.
-
Tiny instruments are inserted through keyhole-sized incisions in the chest.
-
The robot precisely replicates the surgeon’s hand movements, allowing for extreme precision, flexibility, and control.
This technique avoids a large chest incision and typically does not require the sternum (breastbone) to be cut, which makes it far less traumatic for the body.
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Bypass Surgery
Robotic technology brings significant advantages for both the patient and the surgeon:
1. Minimally Invasive
Small incisions mean less pain, fewer complications, and minimal scarring. There’s also a reduced risk of infection.
2. Faster Recovery
Patients typically return home in a few days and resume daily activities in 2-3 weeks—much quicker than the 6-8 week recovery after open-heart surgery.
3. Precision and Accuracy
The robotic arms can perform movements with greater dexterity than the human hand, reaching hard-to-access areas with ease.
4. Lower Blood Loss
Smaller incisions and improved visualization reduce the chances of excessive bleeding during surgery.
5. Better Cosmetic Outcomes
Tiny incisions along the side of the chest (instead of the middle) mean no large scar on the chest.
Who is a Candidate for Robotic Bypass Surgery?
Not everyone is eligible for robotic-assisted bypass surgery. Ideal candidates include:
-
Patients with single-vessel disease (especially in the left anterior descending artery)
-
Those who are generally in good health, with no extensive comorbidities
-
Patients who need minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass (MIDCAB) or TECAB
People with multiple blocked arteries or complex heart conditions may still need traditional open-heart surgery.
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
-
Preparation
The patient is put under general anesthesia. Small incisions (usually 3–5) are made between the ribs. -
Robot Setup
A high-tech robotic system, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, is used. The surgeon operates the robot from a control console. -
Harvesting the Graft
A healthy artery (often the internal mammary artery) is detached and prepared to bypass the blockage. -
Bypass Creation
The robotic instruments stitch the artery to the heart, bypassing the blocked section. -
Closing Up
The instruments are removed, and incisions are closed with minimal suturing.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, robotic-assisted bypass surgery comes with potential risks, such as:
-
Bleeding
-
Infection
-
Stroke
-
Heart rhythm problems
-
Need to convert to open surgery in some cases
However, when performed by an experienced surgical team, the risks are significantly lower than those associated with traditional bypass procedures.
The Future of Cardiac Surgery
Robotic-assisted cardiac procedures are a glimpse into the future of heart care. With AI integration, real-time imaging, and data-driven decision-making, the surgical outcomes are becoming more refined. More hospitals across India and the world are now equipped with robotic cardiac surgery systems, making it increasingly accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does robotic bypass surgery take?
The procedure usually takes 3 to 5 hours, depending on the complexity and the number of arteries being bypassed.
2. Is robotic surgery safe?
Yes. Robotic systems are designed with numerous safety checks, and the entire procedure is still controlled by a skilled surgeon. Complication rates are low in experienced hands.
3. Will I need to stay in the ICU?
Yes, most patients are monitored in the ICU for the first 24 to 48 hours after surgery for observation and recovery.
4. How long before I can return to work?
Patients can often return to desk jobs within 2–3 weeks. For physically demanding work, recovery may take 4–6 weeks.
5. Is robotic bypass surgery more expensive?
Yes, due to the high cost of robotic equipment and expertise, the initial cost is higher. However, the shorter hospital stay and quicker recovery can offset some of the expenses.
6. Is this available in India?
Absolutely. Several top-tier hospitals in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad now offer robotic cardiac surgery. Surgeons with robotic training are increasingly available.
7. Will I need another bypass in the future?
It depends on your overall heart health and lifestyle. Robotic surgery offers results comparable to traditional methods. A healthy lifestyle, regular medication, and follow-ups are key to long-term success.
 +91 96001 07057
+91 96001 07057 Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
