 29 April, 2025
29 April, 2025
Understanding Rheumatic Heart Disease | Dr.Dhamodaran K
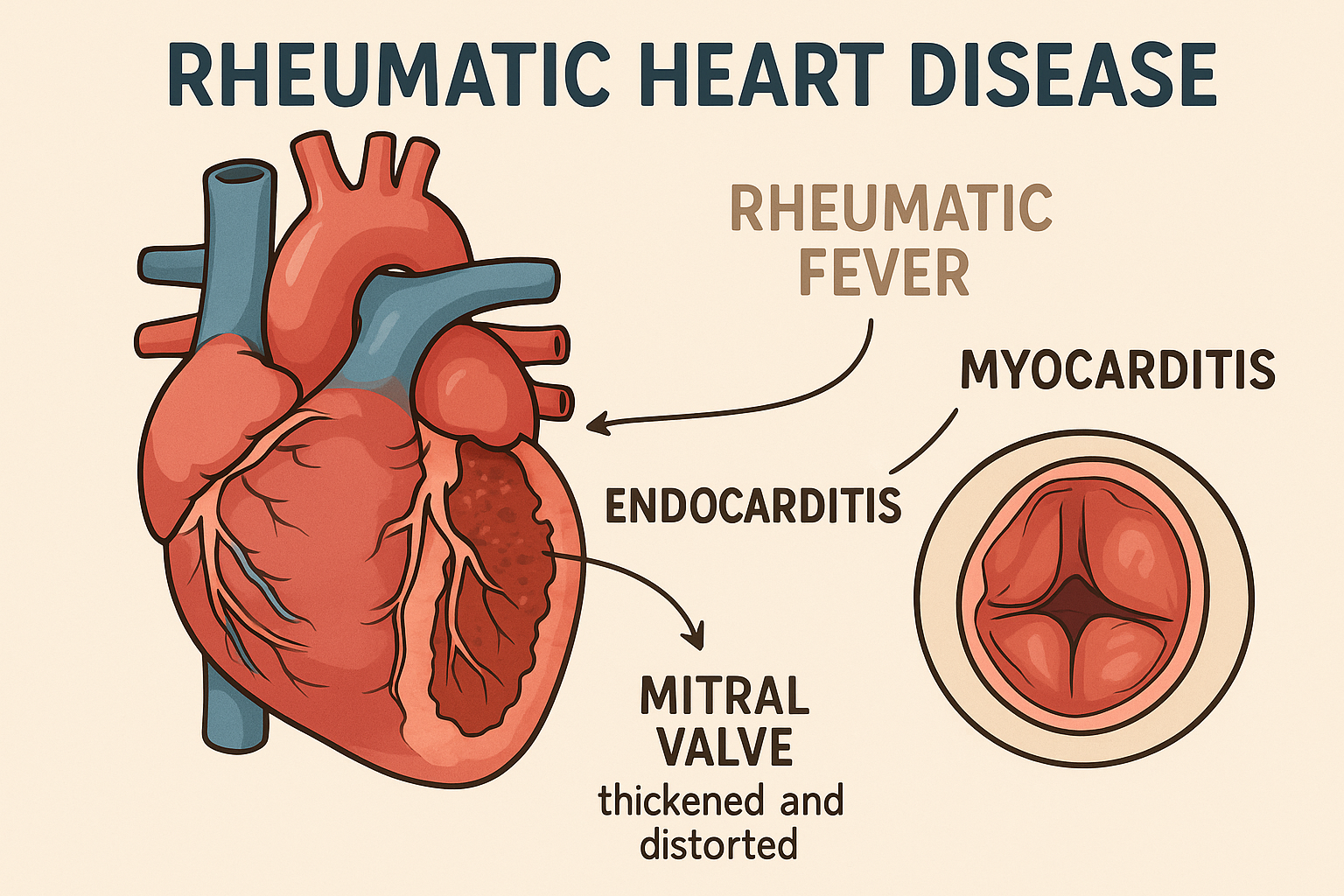
RHD is a chronic heart condition resulting from damage to the heart valves caused by rheumatic fever—a complication of untreated or inadequately treated group A streptococcal (GAS) infections, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. The body’s immune response to these infections can lead to inflammation in the heart, joints, skin, or central nervous system. Repeated episodes of rheumatic fever can cause cumulative damage to the heart valves, leading to RHD .
Causes and Risk Factors
Primary Cause
The primary cause of RHD is rheumatic fever, which stems from an abnormal immune response to GAS infections.
Risk Factors
-
Age: Children aged 5–15 are most susceptible.
-
Socioeconomic Status: Poverty, overcrowding, and limited access to healthcare increase risk.
-
Geographical Location: Higher prevalence in developing countries and marginalized communities .
Symptoms of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity and progression of the disease:
-
Shortness of breath, especially during exertion or when lying down.
-
Fatigue and weakness.
-
Chest pain or discomfort.
-
Swelling of the legs, ankles, and feet.
-
Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeats.
-
Fainting or dizziness.
In some cases, symptoms may not appear until the disease has progressed significantly.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessing symptoms and listening for heart murmurs.Osmosis
-
Echocardiogram: Ultrasound imaging to evaluate heart valve damage.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects irregular heart rhythms.
-
Chest X-ray: Identifies heart enlargement or fluid in the lungs.
-
Blood Tests: Detects inflammation and streptococcal antibodies.
Treatment Options
1. Medical Management
-
Antibiotic Therapy: Long-term penicillin prophylaxis to prevent recurrent rheumatic fever.
-
Anti-inflammatory Medications: Aspirin or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
-
Heart Failure Management: Medications like diuretics, beta-blockers, or ACE inhibitors.
2. Surgical Interventions
-
Valve Repair or Replacement: In severe cases, damaged valves may need surgical correction.
-
Balloon Valvotomy: A minimally invasive procedure to open narrowed valves.
Prevention Strategies
Primary Prevention
-
Prompt Treatment of Strep Throat: Early antibiotic therapy to prevent rheumatic fever.
Secondary Prevention
-
Regular Antibiotic Prophylaxis: Ongoing penicillin injections to prevent recurrence.
Tertiary Prevention
-
Comprehensive Care: Managing established RHD to prevent complications.
Recent Advances and Guidelines
The World Health Organization (WHO) has released new guidelines emphasizing the importance of prevention and early diagnosis of RHD. These guidelines advocate for integrated approaches combining primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention strategies to effectively combat RHD .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is rheumatic heart disease contagious?
A1: No, RHD itself is not contagious. However, the initial streptococcal infections that can lead to rheumatic fever and subsequently RHD are contagious.
Q2: Can RHD be cured?
A2: While the damage caused by RHD is permanent, early detection and appropriate treatment can manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
Q3: How often should penicillin injections be administered for secondary prevention?
A3: WHO recommends intramuscular benzathine penicillin G injections every 3–4 weeks for secondary prevention .AHA Journals+2World Health Organization (WHO)+2World Heart Federation+2
Q4: Are there any vaccines available for RHD?
A4: Currently, there is no vaccine for RHD. Prevention focuses on treating streptococcal infections promptly to prevent rheumatic fever.
Q5: What lifestyle changes can help manage RHD?
A5: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, can help manage RHD symptoms.
 +91 96001 07057
+91 96001 07057 Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
Sidharam Heart Clinic Adyar, Gandhi Nagar, Canal Bank Road, Opp.St.Louis School, Adyar, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600020
